 The Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area is a national leader in finance, advanced manufacturing, agriculture and retailing.
The Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area is a national leader in finance, advanced manufacturing, agriculture and retailing.
Medical devices, electronics and processed foods are strong suits recognized globally.
Want the freshest data delivered by email? Subscribe to our regional newsletters.
6/18/2015 2:23:55 PM
Tim O'Neill
This spring, we learned that industries and occupations do not have an equal gender balance in the Seven-County Twin Cities Metro Area. Male workers, for example, are much more prevalent in construction, architecture and engineering, protective services, and computer occupations; while female workers are much more prevalent in healthcare practitioner and support occupations, personal care and service, and education.
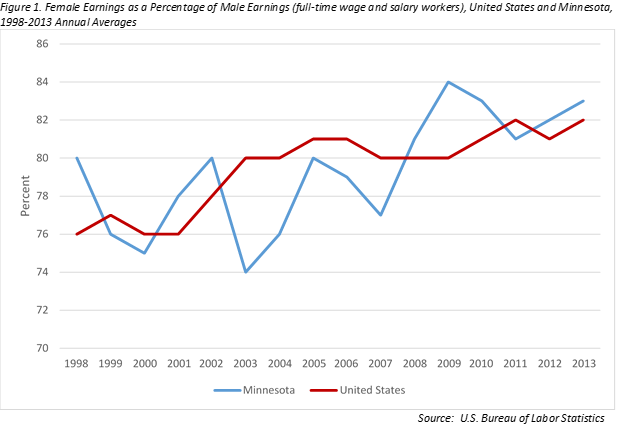
Beyond industry and occupational imbalances, there are large differences in pay for men and women. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, women in Minnesota who were full-time wage and salary earners had average median weekly earnings of $790 in 2013. This was 83 percent of the $956 their male counterparts earned on average each week. As such, Minnesota had the 18th highest ratio for female to male earnings in the nation.
While this ranking is nothing to write home about, the ratio is on the rise in Minnesota. In 2003, for example, women in Minnesota earned only 74 percent of what men did. By 2009, women earned 84 percent of what men did, before settling at 83 percent in 2013 (see Figure 1).
When zooming into the Seven-County Twin Cities Metro Area, we turn to the U.S. Census Bureau's Quarterly Workforce Indicators (QWI) tool. This data tool derives employment and wage information from a number of sources, including Unemployment Insurance (UI) earnings data, Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW) data, Business Dynamics Statistics (BDS), and demographic data sources. As such, the results cannot be compared with Current Population Survey (CPS) data, as was used in Figure 1.
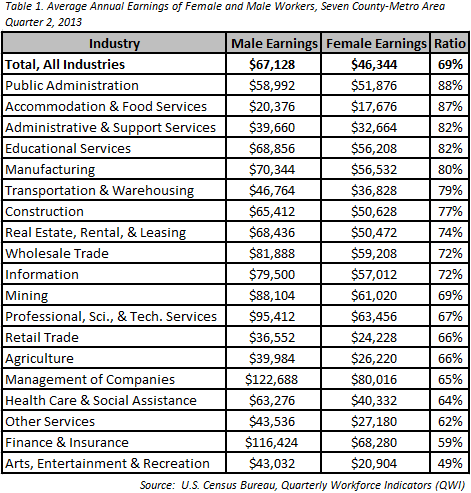
According to QWI data, from the second quarter, 2013, females in the Twin Cities area earned approximately 69 percent of what males did. One can also analyze this ratio for the major industry sectors. For example, females earned nearly 90 percent of what males did in Public Administration. On the other end of the spectrum, females only earned about half of what males did in Arts, Entertainment, and Recreation (see Table 1).
While pay disparities are certainly present within the Seven-County Metro Area, Minnesota, and the nation, there may be factors that account for these differences beyond gender. These may include educational attainment, prior work experience, specific occupations held, and the size of companies people work for. To see what wages people are earning, visit DEED's Occupational Employment Statistics (OES) tool.
Contact Tim O'Neill at 651-259-7401.