
by Steve Hine and Cameron Macht
December 2017
In a tight labor market, immigrants are a vital source of talent for Minnesota employers. Foreign-born workers now account for 10 percent of the state's labor pool.
Increasingly tight labor markets and a growing scarcity of workers are now recognized as two of Minnesota's most significant barriers to sustained economic growth. In the face of these constraints, it has become increasingly evident that immigration has been and will continue to be a vital source of the workforce that employers need to succeed in the state.
After averaging a net gain of just over 40,000 additional labor force participants per year between 1976 and 2000, Minnesota employers could easily tap into a large and growing pool of talented workers. From 2000 to 2016, however, our growth in available workers dropped to less than one-third that, at just over 11,000 new workers per year (see Chart 1).
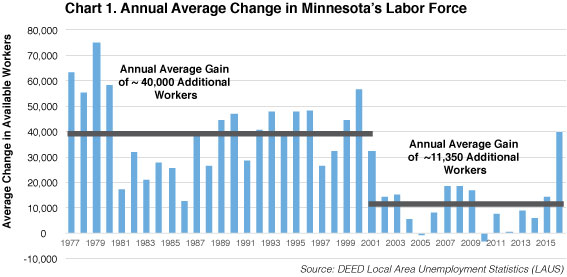
Recently released labor force projections from the Minnesota State Demographic Center suggest this growth will fall further in the years ahead, to an annual average of just over 7,000 additional labor force participants per year between now and 2030. This will make it more challenging for employers to grow, but will also shine a light on the importance of immigration.
Since 2010, the foreign-born labor force in Minnesota has increased by 56,200 people (23 percent growth), while the native-born labor force has increased by 44,400 (1.6 percent growth). This means that more than half of our recent labor force growth has been driven by immigrants. And this will certainly continue to be the case, with immigrants displaying a much younger age profile than the native-born population, which is aging rapidly and exhibiting lower labor force participation rates as retirement picks up.
This article reviews immigration trends to Minnesota, as well as the characteristics of these new Minnesotans. In light of possible restrictions on immigration to the U.S., it is important to understand historical trends and reflect on the possible consequences to Minnesota's labor market and economy. The primary data source for this article is the American Community Survey.
Immigrants have become critical to Minnesota's economy, providing a rapid stream of new workers in the face of an aging native-born workforce. Foreign-born workers now account for 10 percent of the total available labor force in Minnesota, up from 7.5 percent just one decade earlier. In sum, the number of foreign workers jumped from 216,409 in 2006 to 302,879 in 2016.
Minnesota's labor force increased by just over 150,000 workers from 2006 to 2016, a steady 5.2 percent expansion. More than half – 86,470 or 58 percent – of those workers were foreign born. Put another way, the foreign-born labor force expanded by 40 percent from 2006 to 2016, compared with 2.4 percent growth among the native-born workforce.
While labor force participation rates were declining for native-born workers, they were increasing for foreign-born workers. Participation rates were around 71 percent for both groups in 2006, but dropped to 69.1 percent for native-born workers by 2016 and rose to 72.7 percent for foreign-born workers (see Table 1).
Table 1. Labor Force Characteristics of the Native and Foreign Born Population in Minnesota
| - | - | 2006-2016 Change | 2011-2016 Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2011 | 2016 | Number | Percent | Number | Percent | |
| Native Born | |||||||
| Population 16 and Over | 3,754,283 | 3,855,411 | 3,959,481 | 205,198 | 5.5% | 104,070 | 2.7% |
| In Labor Force | 2,673,049 | 2,702,643 | 2,736,001 | 62,952 | 2.4% | 33,358 | 1.2% |
| Participation Rate | 71.2% | 70.0% | 69.1% | -2.1% | blank | -0.9% | blank |
| Employed Workers | 2,534,141 | 2,498,306 | 2,637,014 | 102,873 | 4.1% | 138,708 | 5.6% |
| Unemployed | 136,326 | 202,698 | 98,496 | -37,830 | -27.7% | -104,202 | -51.4% |
| Unemployment Rate | 5.10% | 7.50% | 3.60% | -1.5% | blank | -3.9% | blank |
| Foreign Born | |||||||
| Population 16 and Over | 304,802 | 355,053 | 416,042 | 111,240 | 36.5% | 60,989 | 17.2% |
| In Labor Force | 216,409 | 254,573 | 302,879 | 86,470 | 40.0% | 48,306 | 19.0% |
| Participation Rate | 71.0% | 71.7% | 72.7% | 1.7% | blank | 1.0% | |
| Employed Workers | 202,693 | 229,719 | 285,405 | 82,712 | 40.8% | 55,686 | 24.2% |
| Unemployed | 13,417 | 25,203 | 17,264 | 3,847 | 28.7% | -7,939 | -31.5% |
| Unemployment Rate | 6.2% | 9.9% | 5.7% | -0.5% | blank | -4.2% | blank |
| Source: U.S. Census Bureau, American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates | |||||||
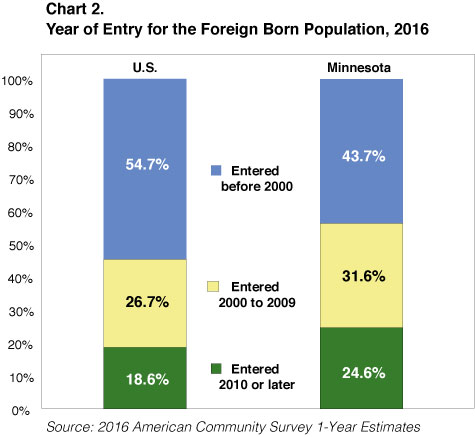
According to the American Community Survey, Minnesota is now home to more than 450,000 foreign-born residents, or about one in every 12 people. Of those, 43.7 percent entered the U.S. before 2000, 31.6 percent came between 2000 and 2009, and the remaining 24.6 percent settled in Minnesota since 2010. That made Minnesota's foreign-born population "newer" than in the rest of the United States, where 54.7 percent entered prior to 2000 and just 18.6 percent entered since 2010 (see Chart 2).
One challenge to assimilating into a new culture is language, but many new Minnesotans have made headway. About 81 percent of foreign-born residents in Minnesota speak a language other than English, but many of them can also speak English. About 45.3 percent reported they speak English less than "very well," compared with 49.1 percent of foreign-born residents nationwide.
Perhaps surprisingly, a notable portion of Minnesota's foreign-born population is well educated, with about one-third (32.6 percent) of foreign-born adults age 25 and over holding a bachelor's degree or higher, which is right in line with native-born Minnesotans (35 percent). In each case, Minnesota was above the comparable educational attainment levels for both foreign- (30 percent) and native- (31.6 percent) born residents nationwide.
It is equally important, however, to note that nearly half (45.8 percent) of foreign-born Minnesotans have a high school diploma or less, including 27.1 percent that are not high school graduates. That compared with just 30.8 and 4.9 percent of natives, respectively.
For foreign-born residents who were not U.S. citizens, this jumps to 52.7 percent with a high school diploma or less, including 34.4 percent without a high school diploma. This is a sizeable number and shows that many immigrants need access to education to be prepared for the workforce, where jobs for high school graduates are increasingly difficult to fill.
Another big gap between native- born and foreign-born is in the percentage of residents who have attended some college or earned an associate degree. Just over 34 percent of native-born Minnesotans have some college or an associate degree, compared with just 21.6 percent of foreign-born Minnesotans and just 15.5 percent of foreign-born non-citizens.
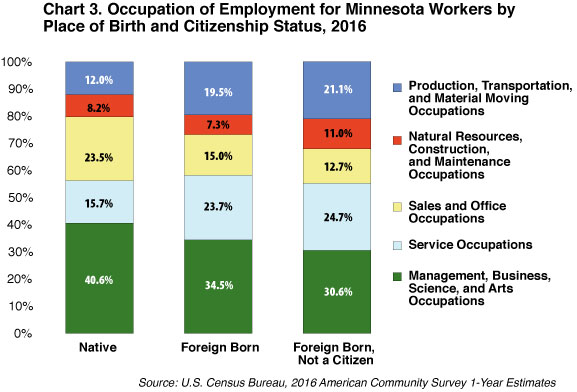
Perhaps in part due to the language and educational barriers described, foreign-born workers were much more likely to work in certain occupational and industry groups than native-born workers. For example, native-born workers were 8.5 percentage points more likely to work in sales and office occupations than foreign-born workers, and 6.1 percentage points more concentrated in management, business, science and arts occupations.
In contrast, foreign-born workers were found more often in service occupations, which include health care support, protective service, food preparation and serving, building and grounds cleaning, and personal care occupations. They were also much more concentrated in production, transportation and material moving occupations. These gaps are even more pronounced for foreign-born workers who are not citizens, who presumably have entered more recently (see Chart 3).
By industry, foreign-born workers were much more likely to be found working in manufacturing, administrative support and waste management services – which includes temporary staffing services – and leisure and hospitality. In contrast, immigrants were less likely to be employed in retail trade, public administration, construction, and finance, insurance and real estate.
Not surprisingly, some detailed occupations have very high shares of foreign-born workers (see Table 2). Some of these occupations are already showing critical workforce shortages in Minnesota, including nursing, psychiatric, home health and personal care aides, as well as computer and construction-related occupations. Understanding which industries and occupations our foreign-born workers disproportionately support becomes even more crucial with recent overtures to restrict immigration.
Table 2. Top Occupations Employing Foreign Born Workers in Minnesota, 2015
| Occupation | Foreign Born Employment | Foreign Born Share of Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Janitors and Cleaners, Except Maids and Housekeeping Cleaners | 10,880 | 16.7% |
| Cooks | 10,272 | 18.8% |
| Miscellaneous Assemblers and Fabricators | 9,624 | 26.4% |
| Nursing, Psychiatric and Home Health Aides | 8,710 | 15.4% |
| Personal Care Aides | 7,930 | 18.4% |
| Software Developers, Applications and Systems Software | 7,622 | 30.3% |
| Maids and Housekeeping Cleaners | 7,064 | 26.2% |
| Postsecondary Teachers | 6,261 | 19.3% |
| Miscellaneous Agricultural Workers | 4,949 | 17.9% |
| Biomedical Engineers | 4,847 | 22.3% |
| Hand Packers and Packagers | 4,546 | 35.8% |
| Physicians and Surgeons | 3,929 | 22.0% |
| Packaging and Filling Machine Operators and Tenders | 3,249 | 38.0% |
| Computer Programmers | 2,942 | 23.0% |
| Miscellaneous Media and Communication Workers | 2,835 | 63.6% |
| Miscellaneous Personal Appearance Workers | 2,726 | 64.2% |
| Butchers and Other Meat, Poultry, and Fish Processing Workers | 2,646 | 39.5% |
| Computer and Information Systems Managers | 2,598 | 16.8% |
| Computer Systems Analysts | 2,498 | 17.8% |
| Taxi Drivers and Chauffeurs | 2,093 | 31.3% |
| Roofers | 1,775 | 30.7% |
| Source: 2011-2015 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates | ||
Wherever they work, these new Minnesotans are a vital part of the state's economy, providing rapid growth to an otherwise aging and slowing labor force. In the years ahead, it is likely that labor force constraints will require that every employer consider our young and growing immigrant population as a source of the workforce they will need.
Diminished labor force growth has been obvious in recent years, and it is expected to fall further in the years ahead. Job growth will be constrained by the lack of an available workforce, especially in areas of Greater Minnesota that also have a lower share of both immigrants and minorities. And even with success in attracting new workers, we might not have all the workers that employers will need. Hence, we should also take steps to ensure that we're making the most of the workers we have by removing frequent impediments to work.
Minnesota's immigrant population has been a crucial source of the workforce our state needs to continue to grow, and this is only expected to intensify in the years ahead. It is critically important, therefore, that we take steps to reduce any barriers that our foreign-born residents face in fully participating in our labor markets. Only by doing so can we hope to continue the economic success that our state has been known for.