 Southeast Minnesota is a health care and agricultural powerhouse. The region is home to the renowned Mayo Clinic and some of the world's most recognized food companies and brands.
Southeast Minnesota is a health care and agricultural powerhouse. The region is home to the renowned Mayo Clinic and some of the world's most recognized food companies and brands.
Advanced manufacturing is especially strong here, with machinery, chemicals, and electronics among the top products.
Want the freshest data delivered by email? Subscribe to our regional newsletters.
9/28/2018 1:00:00 PM
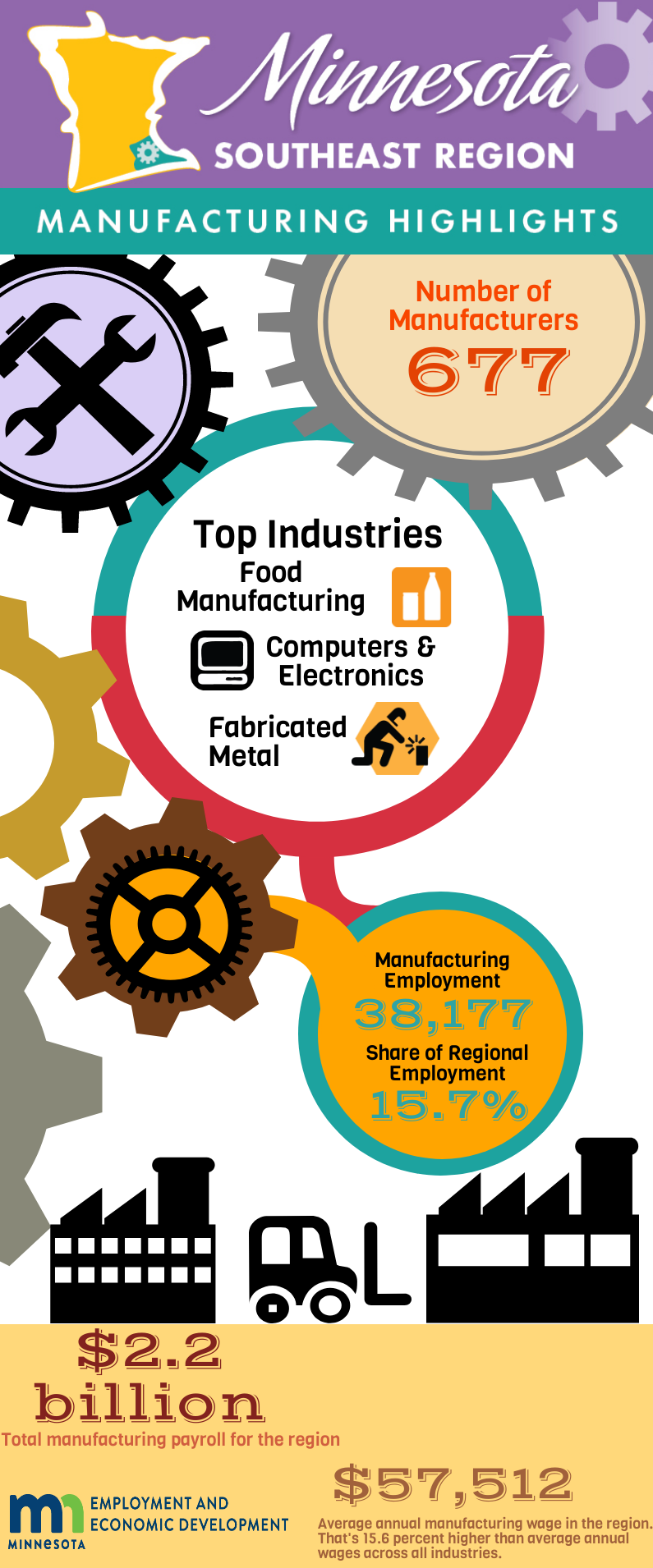 With 38,177 jobs at 677 establishments, manufacturing is the second largest employing industry in the 11-county Southeast Minnesota economic development region, behind health care and social assistance. Manufacturing accounts for 15.7 percent of total employment in Southeast, which is much more concentrated than in the state as a whole, where 11.2 percent of total jobs are in manufacturing.
With 38,177 jobs at 677 establishments, manufacturing is the second largest employing industry in the 11-county Southeast Minnesota economic development region, behind health care and social assistance. Manufacturing accounts for 15.7 percent of total employment in Southeast, which is much more concentrated than in the state as a whole, where 11.2 percent of total jobs are in manufacturing.
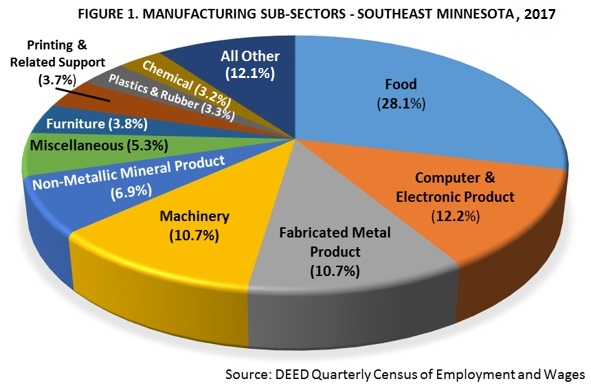
Though food manufacturing, with 10,726 jobs, is the largest subsector, the manufacturing industry is diverse. Food manufacturing is followed by computer and electronic products, fabricated metal product, and machinery manufacturing, all three of which had over 4,000 jobs. The region also had between 1,400 and 2,640 jobs in nonmetallic mineral product, miscellaneous, furniture and related product manufacturing, and printing and related support activities. Altogether, these eight subsectors make up 81.3 percent of all manufacturing jobs in the region (Figure 1).
Southeast Minnesota has just over 8.5 percent of total employment in the state, but nearly 12 percent of the state’s jobs in manufacturing. The region accounts for 25.3 percent of the state’s nonmetallic mineral product manufacturing employment, 24.4 percent of textile product mills, and 22.6 percent of the food manufacturing jobs in the state, leading to location quotients of 3.0, 2.9 and 2.7, respectively.
The region also shows a higher concentration of jobs in furniture and related products, machinery, computer and electronic product, chemical, and fabricated metal product manufacturing compared to the state as a whole.
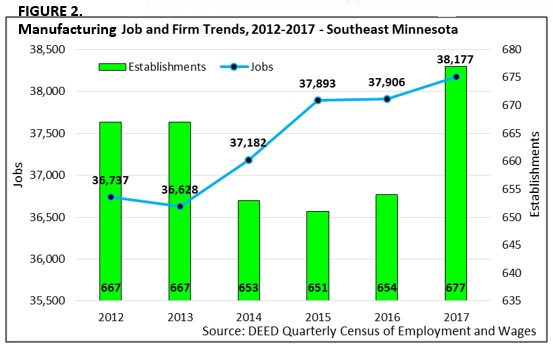
The region saw steady job growth from 2012 to 2017, with manufacturers adding 1,440 jobs during this time (+3.9%), including a gain of 271 jobs (+0.7%) in just the last year. This was a strong recovery from the job losses suffered during the recession, when manufacturing employment fell to a low of 36,628 jobs in 2013. However, manufacturers still have not regained prerecession employment levels, when there were nearly 41,000 manufacturing jobs in 2007 (Figure 2).
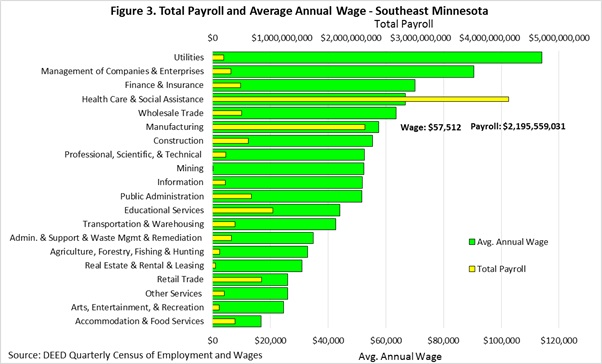
In addition to jobs, manufacturing is also the second largest contributor to the regional economy in terms of payroll, again behind health care and social assistance. Manufacturing payroll almost reached $2.2 billion in 2017, accounting for 18.2 percent of the total payroll, an increase of 15.4 percent since 2012. Average annual wages were also high at $57,512, which is 15.6 percent higher than the average wages across all industries and 11 percent higher than in 2012 (Figure 3).
Contact Mark Schultz.