 Southeast Minnesota is a health care and agricultural powerhouse. The region is home to the renowned Mayo Clinic and some of the world's most recognized food companies and brands.
Southeast Minnesota is a health care and agricultural powerhouse. The region is home to the renowned Mayo Clinic and some of the world's most recognized food companies and brands.
Advanced manufacturing is especially strong here, with machinery, chemicals, and electronics among the top products.
Want the freshest data delivered by email? Subscribe to our regional newsletters.
8/8/2019 4:00:00 PM
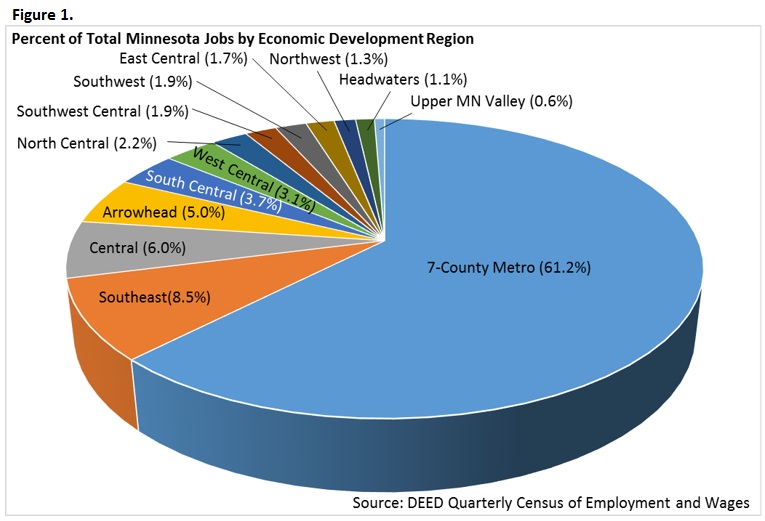
Southeast Minnesota accounts for about 8.5 percent of the total jobs in the state, ranking second in total jobs behind the seven-county metro region, which accounts for 61.2 percent of statewide jobs (Figure 1). The region also comes in second in three other employment categories, including the number of employer establishments, total payroll, and average annual wages. In all, the Southeast region makes up 7.2 percent of the total establishments (12,543 establishments), 7.6 percent of total payroll (a little less than $12.8 billion), and has a median annual wage of $52,260. This is 23.9 percent lower than the seven-county metro and 10 percent lower than the annual wages across all industries statewide, yet 15 percent higher than Central, the third highest region.
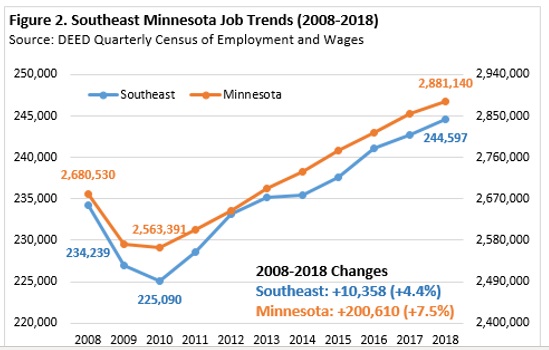
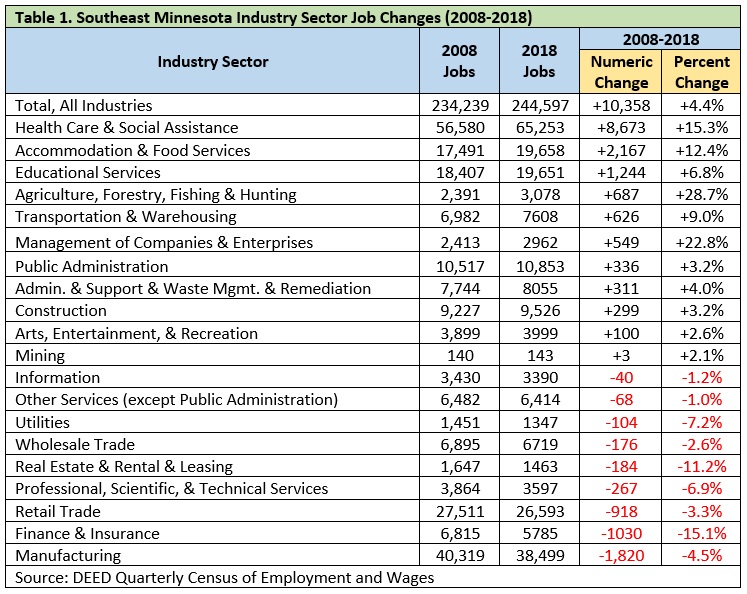
Over the last 10 years, several sectors saw job gains while several others saw job losses. Not surprisingly, health care and social assistance experienced the largest job gain (+8,673), followed by accommodation and food services (+2,167), educational services (+1,244) and agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting (+687). Manufacturing saw the largest decrease in jobs over this time span (-1,820 jobs) despite being one of the powerhouse industries with the second highest number of jobs in the region (15.7 percent). One possible reason for this drop in manufacturing may be the evolution and increased use of technology in the manufacturing process (Table 1).
Contact Mark Schultz.